Ever wondered what really drives the cost of injection molding? Whether you're producing a few hundred or millions of parts, understanding the factors behind injection molding expenses is key to maximizing your budget. From mold design to material selection and production volume, let's dive into how you can control costs while maintaining high-quality results.

What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to create parts with precise shapes. This process works by melting plastic or another material, injecting it into a pre-designed mold, and allowing it to cool and solidify. It’s one of the most widely used techniques for creating high-quality plastic components in large quantities.
How Does the Injection Molding Process Work?
The injection molding process includes several key stages:
Material Preparation: Thermoplastic pellets, such as ABS or polypropylene, are heated until they melt.
Injection Phase: The molten material is injected into a mold at high pressure.
Cooling and Solidifying: The material cools down, hardens, and takes the shape of the mold.
Ejection: The solidified part is ejected from the mold, completing one cycle.
Key Components of the Injection Molding System
Mold: The mold is the core tool. It’s usually made from metal and consists of two halves—Side A and Side B. Side A forms the part’s outer surface, while Side B shapes internal features like ribs or bosses.
Mold Material: Most molds are made from aluminum or steel, depending on the production volume and material being molded.
Design Features: Mold designs include cooling channels, ejector pins, and runner systems to guide material flow.
Injection Molding Machine: The machine includes a hopper for feeding the raw material, a heated barrel to melt it, and a hydraulic or electric mechanism to inject the molten plastic into the mold.
Materials: Thermoplastics, like polypropylene (PP) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), are commonly used in injection molding due to their versatility and recyclability.
Why Injection Molding is Ideal for Mass Production
Fast Production Cycles: A single injection cycle can take less than a minute, making it ideal for large runs.
Cost Efficiency: While initial mold costs are high, the price per part drops dramatically with higher quantities.
High Precision: Injection molding creates parts with tight tolerances and consistent quality, reducing waste.
Factors That Determine Injection Molding Costs
1. Cost of the Tool
Initial Tooling Investment
The mold is often the largest upfront cost in injection molding. It can be 3D printed, made from aluminum, or crafted from steel. Mold pricing varies based on the complexity, size, and material choice:
3D Printed Molds: Best for prototyping or low-volume runs, priced from $100 to $1,000.
Aluminum Molds: Suitable for mid-volume production, costing $2,000 to $5,000.
Steel Molds: Ideal for high-volume production, ranging from $5,000 to over $100,000.
How Mold Complexity Impacts Cost
Complex mold designs can drive costs up. Features like undercuts, part size, and draft angles increase tooling complexity:
Undercuts and Draft Angles: More detailed designs require advanced mold fabrication, which adds to the cost.
Part Size: Larger parts need bigger molds, which are more expensive.
Custom Molds vs. Universal Molds: Custom molds match exact specifications, but universal molds can cut costs if versatility is acceptable.
Mold Lifespan and Durability
Mold lifespan depends on the production volume and material. High-volume molds typically require steel for durability, while low-volume molds can use aluminum or 3D-printed materials:
Low-Volume Molds: Short lifespan, affordable for small production runs.
High-Volume Molds: Durable and long-lasting; steel molds are preferred for extended use.
| Mold Type | Best Use | Estimated Cost |
| 3D Printed Mold | Low-volume runs | $100 - $1,000 |
| Aluminum Mold | Mid-volume runs | $2,000 - $5,000 |
| Steel Mold | High-volume runs | $5,000 - $100,000+ |
2. Equipment Costs
Types of Injection Molding Machines
Different machines offer varying levels of precision, speed, and cost:
Electric Machines: High precision, energy-efficient, but higher initial costs.
Hydraulic Machines: Durable and cost-effective, but less precise.
Hybrid Machines: A mix of both, offering precision and durability but at a higher price.
Machine costs vary:
Small-Scale Production: Desktop machines can cost less than $10,000.
Large-Scale Production: Industrial machines can exceed $100,000.
In-House Production vs. Outsourcing
Businesses must decide whether to buy machines or outsource production. Each option has its pros and cons:
In-House Production: More control over quality and lead times, but requires significant upfront investment.
Outsourcing: Lower capital costs, ideal for small businesses, but may lead to less control over production quality and timing.
| Machine Type | Best Use | Estimated Cost |
| Desktop Machine | Low-volume runs | <$10,000 |
| Industrial Machine | High-volume runs | $50,000 - $200,000+ |
3. Material Costs for Injection Molding
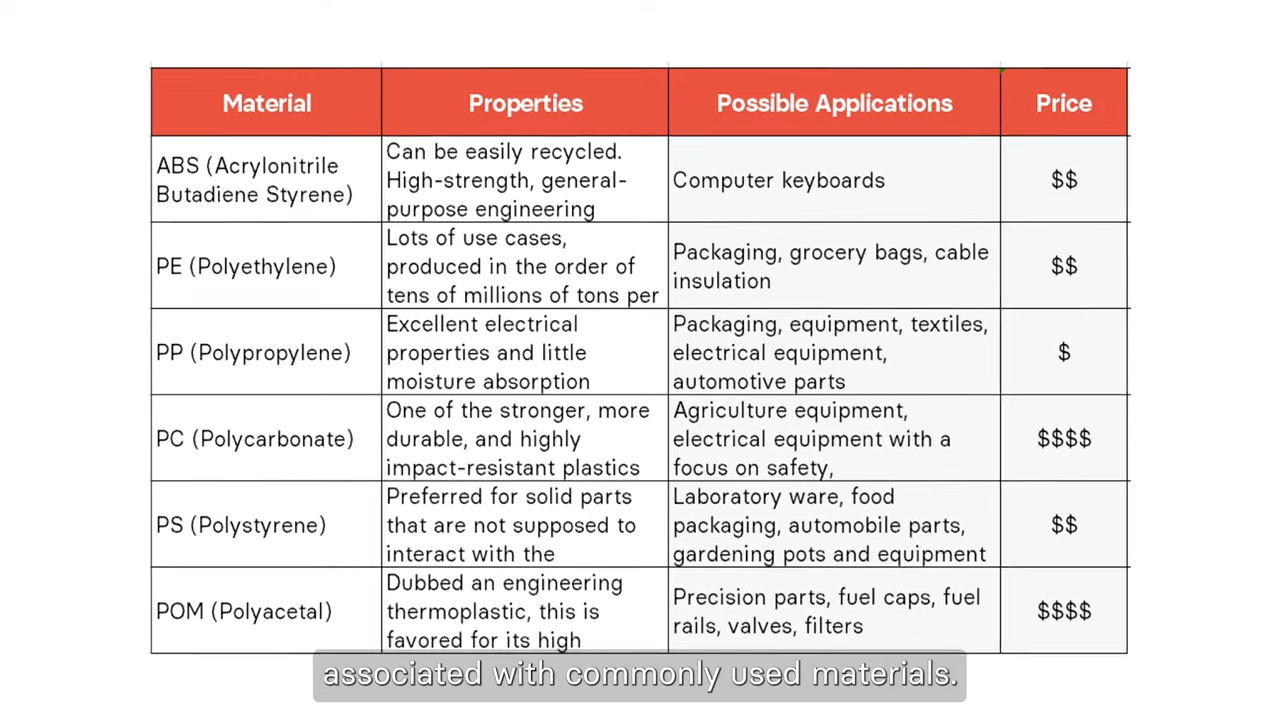
Common Injection Molding Materials and Their Costs
The choice of material significantly affects the cost. Thermoplastics are most commonly used in injection molding, and each has unique properties and pricing:
ABS: Durable, versatile; around $1.30 per kg.
Polypropylene (PP): Lightweight, resistant to chemicals; about $0.90 per kg.
Polyethylene (PE): Flexible, impact-resistant; around $1.20 per kg.
Polycarbonate (PC): Strong, high clarity; costs $2.30 per kg.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Selecting the right material depends on the application. Cost-effectiveness must balance strength, flexibility, and resistance to temperature or chemicals:
Material Properties vs. Cost: Lower-cost materials like PP may be ideal for simple parts, while expensive ones like PC are necessary for high-performance products.
Impact of Additives: Fillers and additives (like colorants or UV stabilizers) increase material costs but may be required based on product specifications.
| Material | Key Features | Price per kg |
| ABS | Durable, lightweight | $1.30 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Flexible, chemical resistant | $0.90 |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Impact resistant, recyclable | $1.20 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | High clarity, strong | $2.30 |
4. Labor and Service Costs
Labor in Injection Molding
Even though much of the injection molding process is automated, labor still plays a role. Key areas where labor costs arise include:
Setup Costs: Initial machine configuration for a specific part.
Repair Costs: Maintenance and part replacements for the machine and mold.
Monitoring Costs: Operators oversee the automation process, ensuring parts are produced correctly.
Outsourcing Service Costs
When outsourcing, labor and service provider fees add to the total cost. These costs include:
Transportation and Logistics: Shipping finished parts from the outsourced provider.
Quality Control: Ensuring the parts meet standards, often requiring additional fees.
Markup: Service providers charge for managing the injection molding process.
Injection Molding Cost by Production Volume
1. Low-Volume Injection Molding
What is Low-Volume Production?
Low-volume production refers to manufacturing smaller quantities, typically between 100 to 1,000 parts. It’s commonly used for prototyping or custom orders where large quantities aren’t necessary. Small-batch production is ideal for testing new products before scaling up.
Mold Costs: For low-volume runs, businesses often use 3D printed molds. These are the most cost-effective, typically ranging from $100 to $1,000.
Per-Part Cost: The cost per part is higher in low-volume production because the fixed mold costs are distributed across fewer units. For example, if a mold costs $1,000 and 100 parts are made, each part incurs $10 in mold cost alone.
| Production Volume | Mold Type | Mold Cost | Cost Per Part |
| 100 - 1,000 parts | 3D printed mold | $100 - $1,000 | Higher ($4.5+) |
When is Low-Volume Production Ideal?
Low-volume production is perfect for prototyping new designs or manufacturing limited product runs for market testing. It’s also useful for companies that want flexibility in product adjustments without committing to high volumes.
2. Mid-Volume Injection Molding
What is Mid-Volume Production?
Mid-volume production typically ranges between 5,000 to 10,000 units. It strikes a balance between prototyping and full-scale manufacturing. This level of production is ideal for small-to-medium businesses looking to produce a product in moderate quantities.
Cost Breakdown for Mid-Volume Production
Mold Costs: Machined aluminum molds are commonly used for mid-volume production because they offer a good compromise between cost and durability. These molds cost between $2,000 to $5,000.
Mold Wear and Tear: Aluminum molds can handle up to several thousand parts before wear and tear begin affecting quality. This durability helps control long-term costs.
| Production Volume | Mold Type | Mold Cost | Cost Per Part |
| 5,000 - 10,000 | Machined aluminum | $2,000 - $5,000 | Moderate ($3) |
3. High-Volume Injection Molding
What is High-Volume Production?
High-volume production refers to the manufacture of tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of parts. This is the most cost-effective method for large-scale production runs, ideal for industries like automotive and consumer goods.
Cost Efficiency of High-Volume Production
Steel Molds: High-volume projects require steel molds, known for their durability and ability to handle repeated production cycles. These molds cost more upfront, ranging from $5,000 to over $100,000, but they last significantly longer.
Lower Per-Part Cost: As production volumes increase, the per-part cost decreases dramatically because fixed mold costs are spread across thousands or even millions of units.
| Production Volume | Mold Type | Mold Cost | Cost Per Part |
| 10,000+ parts | Steel mold | $5,000 - $100,000+ | Low ($1.75) |
Key Factors to Consider for High-Volume Projects
Machine Choice: For high-volume runs, the choice of machine (electric, hydraulic, or hybrid) can impact efficiency and cost.
Material Selection: Choosing the right material helps maintain durability and lower costs over large production cycles.
How to Reduce Injection Molding Costs
1. Optimize Mold Design
Design for Manufacturing (DfM) Principles
Applying DfM principles can significantly reduce injection molding costs by simplifying the mold and part design:
Eliminating Unnecessary Features: Removing complex geometries, undercuts, or unnecessary textures reduces the complexity of the mold, lowering both manufacturing time and material costs.
Simplifying Mold Design: Features like steep draft angles or intricate internal cavities increase costs. Simplified designs reduce the need for advanced mold fabrication techniques, making molds cheaper and faster to produce.

Using Universal Molds
Universal molds are often a cost-effective alternative to custom molds:
When to Use Universal Molds: Universal molds are ideal when parts have similar design requirements, allowing the same mold to be reused across different projects.
Cost Savings: Self-mating parts and simplified designs can drastically reduce the need for multiple molds. One universal mold can lower tooling costs by eliminating the need for creating separate molds for each unique part.
| Mold Design Strategy | Benefits |
| Eliminating unnecessary features | Reduced complexity and cost |
| Universal molds | Fewer molds, lower tooling costs |
2. Material Selection and Optimization
Choosing Lower-Cost Materials
Selecting the right material is key to reducing costs without compromising performance:
Balancing Cost and Performance: Materials like ABS and polypropylene are widely used due to their low cost and good performance characteristics. ABS costs about $1.30 per kg, while polypropylene is even cheaper at $0.90 per kg.
When to Use Premium Materials: For parts that need high heat or impact resistance, higher-cost materials like polycarbonate may be necessary despite their higher price.
Material Waste Reduction
Minimizing material waste can significantly lower costs:
Optimizing Wall Thickness: Thinner walls reduce material use without affecting part strength, provided the design supports it.
Using Recycled Plastics: Incorporating recycled plastics into the manufacturing process lowers material costs and improves sustainability. Recycled thermoplastics offer similar properties at a lower price point.
| Material Selection Strategy | Benefits |
| Choosing lower-cost materials | Reduced per-part cost |
| Recycled plastics | Lower material costs, sustainability |
3. Increase Production Volume
Economies of Scale in Injection Molding
Producing higher volumes helps distribute fixed costs across more parts, reducing the cost per unit:
Larger Batches Lower Costs: As production volume increases, the initial mold and setup costs are spread across a larger number of parts, driving down the per-part cost.
Balancing Production Needs: While high-volume production offers lower costs per part, it's important to balance production volumes with actual demand to avoid unnecessary inventory costs.
Batching Similar Projects Together
Combining similar projects can maximize efficiency:
| Strategy | Cost Savings |
| Increasing production volume | Reduced cost per part through economies of scale |
| Batching similar projects | Spreading fixed costs across more units |
4. Embrace 3D Printed Molds for Prototyping
When to Use 3D Printed Molds
3D printed molds are a cost-effective solution for small production runs or prototyping:
Short Runs and Prototyping: 3D printing can produce molds quickly and affordably for short production cycles, eliminating the need for costly metal molds during the prototyping phase.
Cost Advantages: The upfront cost of 3D printed molds is far lower than traditional aluminum or steel molds, often ranging from $100 to $1,000, making it ideal for rapid iterations and small-batch production.
Limitations of 3D Printing in Injection Molding
While 3D printed molds offer cost savings, they also come with limitations:
Durability: 3D printed molds are not as durable as metal molds, making them less suitable for high-volume production.
Limited to Simple Designs: More complex designs may still require traditional CNC-machined molds for accuracy and durability.
| 3D Printed Molds | Benefits and Limitations |
| Benefits | Low cost, fast production for short runs |
| Limitations | Limited durability, simple designs only |
Injection Molding Cost Calculator Tools
How to Estimate Your Injection Molding Costs
Estimating injection molding costs can be complex, but several online tools simplify the process. These tools use inputs like part size, material, mold complexity, and production volume to give cost estimates.
Overview of Popular Online Cost Estimators
Several cost estimator tools can help you calculate your injection molding expenses:
CustomPart: This tool allows users to input various part details to get quick cost estimates. It’s user-friendly and offers a breakdown of material, mold, and production costs.
Protolabs: Known for rapid prototyping, Protolabs offers a calculator that gives precise quotes based on production volume and material selection. It’s especially helpful for those looking to get parts quickly.
ICOMold: This estimator provides detailed quotes based on CAD models, allowing users to upload designs and receive instant feedback. It's great for more complex projects that need accurate cost analysis.
| Tool | Features |
| CustomPart | Fast estimates for materials, mold, labor |
| Protolabs | Instant quotes, rapid prototyping options |
| ICOMold | CAD-based quotes for complex part designs |
Getting Quotes from Service Providers
Once you've used a cost calculator to get an estimate, reaching out to service providers for quotes can give you a clearer picture of actual costs.
What to Look for in Quotes and Service Agreements
When reviewing quotes from injection molding providers, it’s important to pay attention to several factors:
Setup Fees: Some providers charge additional fees for machine setup or mold preparation.
Lead Times: Look for realistic lead times that fit your project timeline. Faster services often come at a premium.
Quality Guarantees: Ensure the service provider guarantees part quality, including tolerance, finish, and material accuracy.
Tips for Negotiating with Suppliers
Negotiating better rates can lower your overall injection molding cost:
Bundle Orders: Combining multiple projects into one larger order can help spread fixed costs, giving you better per-part pricing.
Request Multiple Quotes: Getting quotes from different suppliers allows you to compare prices and negotiate terms.
Flexible Lead Times: If you have flexible deadlines, you may be able to negotiate lower costs by allowing the provider to fit your order into their schedule.
| Key Factors to Consider | Why They Matter |
| Setup Fees | Affects upfront costs |
| Lead Times | Impacts project timelines |
| Quality Guarantees | Ensures consistent part quality |
| Negotiation Tips | Helps lower costs through bundling or flexible deadlines |
Conclusion: Injection Molding Cost
Injection molding cost is influenced by several key factors, including mold design and material selection, equipment costs, production volume, and labor expenses. To minimize injection molding expenses without sacrificing quality, it's important to apply Design for Manufacturing (DfM) principles, select cost-effective materials, and optimize production volumes. Using universal molds or 3D printed molds for short runs, and combining projects to increase efficiency, are also effective ways to keep costs down.
If you're planning an injection molding project, consider cooperate with TEAM MFG. For more tailored advice or complex designs, contact professional services to get expert guidance and optimize your production process.
FAQs: Injection Molding Costs
What's the typical cost range for injection molding tooling?
Low complexity molds: $2,000 - $25,000
Medium complexity: $25,000 - $100,000
High complexity: $100,000 - $1,000,000+
How does production volume affect per-unit cost?
Higher volumes generally lower per-unit costs
Example: 1,000 units might cost $10/unit, while 100,000 units could drop to $1/unit
What's the most cost-effective material for injection molding?
Polypropylene (PP) is often cheapest
ABS offers a good balance of cost and performance
Material choice depends on specific part requirements
How much can 3D printed molds save on prototyping costs?
What's the break-even point for in-house vs. outsourced production?
Varies widely based on part complexity and volume
General rule: In-house becomes cost-effective at 10,000+ parts annually
How much do material waste and runners add to overall costs?
What's the cost impact of part design complexity?
Simple parts might cost 25-50% less to produce than complex ones
Each additional feature (undercuts, textures, etc.) increases mold and production costs













