Milling machines are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, but which type suits your needs? Should you choose a horizontal or vertical milling machine? These two machine types have distinct differences that impact performance and cost. Selecting the right one can make all the difference in your production efficiency.
In this post, you’ll learn the key features of both horizontal and vertical milling machines. We'll explore their pros, cons, and applications to help you make an informed decision for your machining needs.

What is Mill?
Milling is a machining process where rotating cutting tools remove material from a stationary workpiece. This method is essential in manufacturing parts with precise shapes and sizes. Milling machines help industries like automotive, aerospace, and tool-making efficiently produce components. Milling is versatile, capable of cutting metals, plastics, and other materials.
Types of Milling Machines
Horizontal Milling Machines
Horizontal milling machines position their spindle parallel to the worktable. This design allows them to handle heavier, larger materials and perform deep cuts efficiently. They are ideal for industries where speed, strength, and high-volume production are crucial, such as automotive and aerospace.
Vertical Milling Machines
Vertical milling machines have a spindle oriented perpendicular to the worktable. They are better suited for precision work, intricate designs, and smaller parts. Commonly found in metalworking and prototyping, these machines are highly versatile and easier to operate for complex tasks.
Other Types of Milling Machines
There are also other types of milling machines:
Universal Milling Machines: Equipped with both horizontal and vertical spindles, offering flexibility for various tasks.
Turret Milling Machines: Allow for more movement in different directions, suitable for smaller, more detailed work.
Bed Milling Machines: Fixed worktable design, used for larger, heavier workpieces.
Horizontal Milling Machines
Definition and Key Features
Horizontal milling machines feature a spindle mounted parallel to the worktable. They excel in heavy-duty cutting operations and handling large workpieces. Their robust design allows for:
Simultaneous use of multiple cutters
Efficient material removal
Enhanced stability during deep cuts
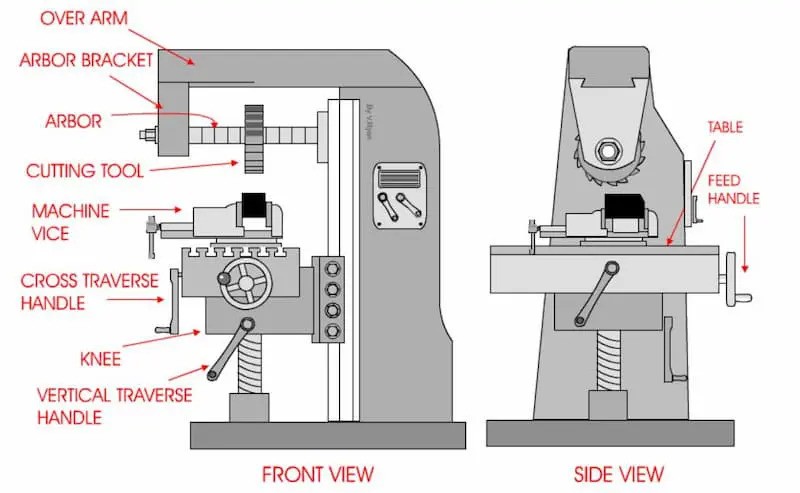
Image Source Fractory
Spindle Orientation and Implications
The horizontal spindle orientation offers several advantages:
Table and Workpiece Movement
Horizontal mills typically employ:
A rotary table for multi-angle approaches
Linear movements along X, Y, and Z axes
Robust clamping systems for secure workpiece holding
Cutting Tools and Operations
Face Mills
Slab Mills
Side and Face Mills
Chip Removal and Cooling
Horizontal mills excel in chip management:
Gravity-assisted chip evacuation
Improved coolant access to cutting zones
Reduced risk of chip recutting
Versatility and Setup Complexity
While offering high versatility for complex parts, horizontal mills often require:
Feed Control
| Feature | Description |
| Automatic Feed | Precise, consistent material removal |
| Manual Feed | Greater operator control for specialized tasks |
Compatibility with Automation Systems
Horizontal mills integrate well with:
Production Efficiency and Volume
Ideal for high-volume production due to:
Flexibility and Ease of Adjustment
While less flexible than vertical mills, they offer:
Operator Skill Requirements
Operating horizontal mills demands:
Advanced knowledge of machining principles
Expertise in complex setup procedures
Proficiency in CNC programming (for CNC models)
Applications and Benefits of Horizontal Mills
Heavy-duty Machining
Horizontal mills excel in industries requiring robust machining capabilities:
Automotive Industry
Engine blocks: Precise milling of complex internal structures
Transmission housings: Efficient removal of large material volumes
Chassis components: Accurate shaping of high-strength alloys
Aerospace Industry
Wings: Intricate contouring of large, lightweight structures
Spars: High-precision milling of load-bearing components
Fuselage sections: Efficient machining of expansive surface areas
Increased Stability and Accuracy
Horizontal mills offer superior stability, enhancing overall machining accuracy:
Reduced vibration during deep cuts
Improved surface finish quality
Tighter tolerances on complex parts
| Feature | Benefit |
| Robust spindle design | Minimizes deflection during heavy cutting |
| Gravity-assisted chip evacuation | Prevents re-cutting, improving surface quality |
| Multi-point workpiece support | Ensures consistent accuracy across large parts |
Enhanced Tool Life
Horizontal milling machines contribute to extended tool life through:
Efficient chip removal, reducing heat buildup
Improved coolant delivery to cutting zones
Optimal cutting angles, minimizing tool stress
These factors result in:
Reduced tooling costs
Fewer tool changes, increasing productivity
Consistent part quality over longer production runs
Vertical Milling Machines
Vertical milling machines feature a spindle oriented perpendicular to the worktable. This configuration enhances versatility, visibility, and precision for intricate work. The vertical spindle allows easy tool changes and efficient material removal, particularly beneficial for drilling and tapping operations.
Table and Workpiece Movement
These mills typically offer:
X and Y axis table movement
Z axis movement via the spindle or quill
Tilting capabilities on some advanced models for angled cuts
Cutting Tools and Operations
Vertical mills accommodate various cutting tools, each serving specific purposes:
End mills: Versatile for face milling, profiling, and slot cutting
Drills: Used for precise hole-making operations
Taps: Facilitate internal thread creation, often with automated cycles in CNC models

Image Source Fractory
Types of Vertical Mills
Turret Mills (Bridgeport-type or Knee Mills)
These versatile machines suit small to medium-sized parts. They feature a movable knee for vertical adjustment, popular in job shops and prototyping environments.
Bed Milling Machines
Designed for larger workpieces, they have a fixed bed with a moving spindle head, providing enhanced stability for precision work.
Feed Control and Automation Compatibility
Vertical mills offer both manual and automatic feed options. They integrate well with automation systems, including tool changers, pallet systems, and robotic loaders, enhancing productivity and enabling extended unmanned operation.
Production Efficiency and Flexibility
Well-suited for low to medium volume production, these machines excel in environments requiring frequent changeovers. They adapt easily to different machining strategies, making them ideal for diverse part families.
Operator Skill Requirements
Operators need:
Basic to intermediate machining knowledge
Familiarity with various cutting tools and their applications
CNC programming skills for automated systems
Applications and Benefits of Vertical Mills
Versatility and Adaptability
Vertical mills excel in diverse manufacturing environments. They easily switch between different operations, making them ideal for job shops and facilities with varied production needs.
Precision and Detail Work
The vertical spindle configuration allows for excellent visibility and control. This makes these machines particularly suitable for intricate parts requiring high precision.
Prototyping and Custom Work
Their flexibility and ease of setup make vertical mills perfect for:
Smaller Footprint and Cost-effectiveness
Vertical mills generally occupy less floor space than their horizontal counterparts. This, combined with their lower initial cost, makes them an attractive option for:
Smaller shops with limited space
Businesses just starting out
Facilities looking to expand their machining capabilities cost-effectively
| Feature | Benefit |
| Vertical Spindle | Enhanced visibility and control |
| Versatile Tooling | Adaptability to various operations |
| Compact Design | Efficient use of shop space |
| Lower Initial Cost | Accessibility for smaller businesses |
Key Differences between Horizontal and Vertical Mills
| Aspect | Horizontal Mills | Vertical Mills |
| Spindle Orientation | Parallel to worktable | Perpendicular to worktable |
| Cutting Tools | Shorter, thicker (e.g., slab mills, face mills) | Longer, thinner (e.g., end mills, drills, taps) |
| Ideal Applications | Large workpieces, complex parts, high-volume production | Smaller parts, precision work, versatile operations |
| Setup Complexity | More complex, time-consuming | Simpler, more intuitive |
| Surface Finish | Consistent on large, flat surfaces | Excellent for intricate details |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Maintenance | More complex | Simpler |
| Workpiece Accessibility | Less accessible, multi-side machining capability | Better visibility and access |
| Chip Evacuation | Gravity-assisted, efficient | Can accumulate at cutting point |
| Tool Life | Generally longer due to better cooling | May require more frequent changes |
| Machining Accuracy | Superior for large surfaces | Excellent for smaller, intricate parts |
| Machine Footprint | Larger floor space, efficient vertical space use | Smaller footprint, space-efficient |
Milling Machine Performance Metrics
Understanding milling machine performance metrics is crucial for selecting the right equipment for specific manufacturing needs. These metrics vary between horizontal and vertical mills, impacting their suitability for different applications.
Key Performance Indicators
| Metric | Horizontal Mills | Vertical Mills |
| Maximum Cutting Depth | Up to 12 inches | Up to 6 inches |
| Table Size | 50 x 20 inches (typical) | 30 x 12 inches (typical) |
| Spindle Speed Range | 500 - 3000 RPM | 1000 - 5000 RPM |
| Power Output | 5 - 15 HP | 2 - 7.5 HP |
Spindle Power and Torque
Horizontal mills generally offer higher spindle power and torque, enabling them to handle heavier cuts and larger workpieces. Vertical mills, while typically less powerful, provide sufficient torque for most general machining tasks.
Table Load Capacity and Travel
Horizontal mills excel in table load capacity, often supporting heavier workpieces. They usually offer greater table travel, facilitating machining of larger parts. Vertical mills, while more limited in these aspects, provide ample capacity for most common machining operations.
Overall Machine Dimensions and Weight
Horizontal mills tend to be larger and heavier, requiring more floor space. This increased size contributes to their stability during heavy cutting operations. Vertical mills, being more compact, offer space-saving advantages in smaller workshops.
Compatibility with CNC Systems
Both horizontal and vertical mills integrate well with CNC systems. Modern CNC controllers enhance the capabilities of both types, offering:
Typical Applications
Horizontal Mills:
Heavy-duty machining of large parts
Automotive and aerospace components
Multi-side machining in a single setup
Vertical Mills:
Precision work on smaller parts
Prototyping and custom machining
General-purpose milling tasks
Choosing the Right Mill for Your Needs
Selecting the right milling machine is critical for ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness in your manufacturing process. Whether you choose a horizontal or vertical milling machine depends on several factors, all of which should align with your specific application requirements.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Milling Machine
Workpiece Size and Complexity: Horizontal mills are better for large, heavy parts, while vertical mills are ideal for small, intricate work.
Required Accuracy and Surface Finish: Vertical mills provide greater precision for detailed tasks, while horizontal mills excel in rough material removal.
Production Volume: For high-volume production, horizontal mills offer faster material removal, while vertical mills are suitable for smaller batch runs.
Available Floor Space and Budget: Vertical mills take up less space and are more affordable, while horizontal mills often require more space and a higher initial investment.
Advantages of Horizontal Mills for Specific Applications
Horizontal milling machines provide better stability and material removal rates for heavy-duty tasks. These advantages make them well-suited for:
Large workpieces: Handling bulky parts requiring deep cuts.
Multiple-side machining: Complex parts needing work from different angles without frequent retooling.
Heavy material removal: Large production runs in industries like automotive and aerospace.
Advantages of Vertical Mills for Specific Applications
Vertical mills are versatile and cost-effective, offering high precision and ease of use for smaller tasks. They excel in:
Precision work: Perfect for intricate cuts and fine surface finishes.
Prototyping and custom jobs: Ideal for detailed, one-off designs or small batch production.
Lower-budget operations: Offering a smaller footprint and lower upfront costs, making them accessible to small shops.
Specific Application Scenarios and Case Studies
Complex Cavity Machining: Horizontal mills handle complex cavities by allowing for deep cuts and efficient chip removal, which is essential in industries like mold-making.
Stepped Surface Machining: Vertical mills are excellent for machining stepped surfaces, where precision and fine adjustment are key.
High-Hardness Material Machining: Horizontal mills are preferable for machining high-hardness materials like steel, due to their greater cutting power.
Small-Batch, High-Variety Production: Vertical mills shine in small-batch, high-variety production settings, where frequent setup changes are necessary.
Automation Line Retrofitting: For companies looking to retrofit automation lines, horizontal mills offer compatibility with advanced automation systems, enhancing productivity in mass production.
| Application | Recommended Mill Type | Key Benefit |
| Complex Cavity Machining | Horizontal | Deep cuts, efficient chip removal |
| Stepped Surface Machining | Vertical | Precision and easy adjustment |
| High-Hardness Material Machining | Horizontal | Greater cutting power |
| Small-Batch, High-Variety Production | Vertical | Quick setup changes, detailed machining |
| Automation Line Retrofitting | Horizontal | High compatibility with automation systems |
Choosing the right mill depends on balancing your specific needs, budget, and production goals. Both horizontal and vertical mills offer distinct advantages, and selecting the right one can drastically improve your manufacturing efficiency.
Conclusion
Horizontal and vertical milling machines differ mainly in spindle orientation, setup complexity, and application. Horizontal mills are ideal for heavy-duty tasks, while vertical mills excel in precision work. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses is crucial for optimizing performance.
Choosing the right mill depends on your workpiece size, production volume, and accuracy requirements. Both mill types can complement each other in a well-rounded machine shop. By assessing your needs, you can effectively plan and configure your milling resources for maximum efficiency and productivity.












