Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing, creating precise parts in industries like aerospace and automotive. But what makes Sinker EDM different from Wire EDM, and which is right for your project?
In this post, you'll learn how each EDM type works, including their pros, cons, and best applications. By the end, you'll understand the key factors that make each EDM technique unique and be able to decide which is best suited to your manufacturing needs.
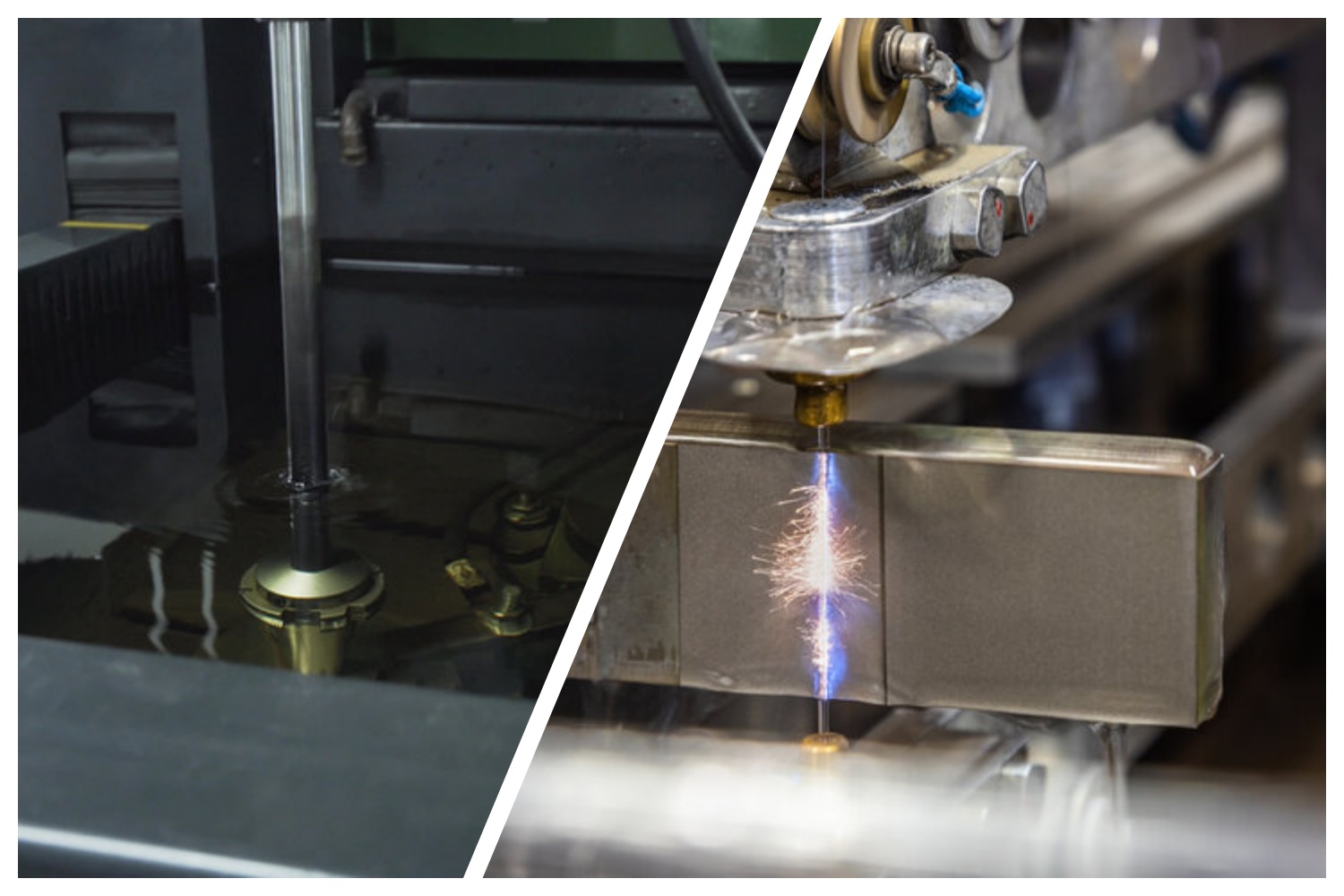
What is Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)?
Electrical Discharge Machining, or EDM, is a highly specialized manufacturing process that uses electrical discharges (sparks) to shape materials. Unlike traditional machining, which relies on physical cutting, EDM relies on controlled sparks to erode and shape metal precisely. This unique approach makes EDM ideal for working on hard metals and achieving high precision in intricate designs.
How EDM Works
The spark erosion process follows a precise sequence. First, two electrodes position near each other, while dielectric fluid fills the gap between them. Computer controls maintain proper spacing throughout the operation.
During material removal, high voltage creates powerful sparks. These sparks generate local temperatures reaching 8,000-12,000°C, melting metal at contact points. The dielectric fluid then washes away debris as the process repeats thousands of times per second.
Key Point: The dielectric fluid plays three essential roles: insulator, coolant, debris remover.
Why EDM is Different from Traditional Machining
| Characteristic | Traditional Machining | EDM |
| Contact Method | Direct tool contact | Non-contact sparks |
| Forces Applied | High mechanical stress | Zero physical force |
| Material Range | Limited by hardness | Any conductive metal |
| Precision Level | Tool-dependent | Micro-level accuracy |
| Heat Impact | Mechanical heat | Controlled thermal effect |
EDM offers significant advantages over traditional methods. It cuts super-hard metals like titanium and tungsten while creating intricate shapes impossible through conventional machining. The process maintains tight tolerances, produces no mechanical stress, and works perfectly on delicate components.
In daily situations, there are two primary types of EDM machines: Sinker EDM and Wire EDM.
What is Sinker EDM?
Sinker EDM, also known as ram EDM or cavity EDM, is a precise machining process used to shape complex 3D cavities in conductive materials.
Sinker EDM Process Overview
Sinker EDM works by placing an electrode and the workpiece in a dielectric fluid. The electrode, often made of graphite or copper, is pre-shaped to match the desired cavity shape. When voltage is applied, the dielectric fluid allows sparks to jump across the narrow gap between the electrode and workpiece. Each spark erodes a small amount of material, shaping the workpiece without direct contact. This process minimizes mechanical stress and allows for high precision in complex geometries.
Components of a Sinker EDM Machine
A typical Sinker EDM machine includes these essential components:
Shaped Electrode: A custom-machined tool that mirrors the shape of the desired cavity. Commonly made of graphite or copper, it’s gradually lowered into the workpiece during the process.
Dielectric Oil: A hydrocarbon-based fluid that insulates the electrode from the workpiece, controlling spark generation and cooling the workpiece by flushing away debris.
Power Source: Provides the electrical energy needed to generate sparks and maintain a controlled erosion rate.
Applications of Sinker EDM
Sinker EDM is particularly suited to industries requiring precision cavities and complex internal geometries, such as:
Mold Making: Creating detailed injection molds, extrusion dies, and stamping dies.
Blind Cavities: Machining internal shapes that don’t pass through the entire material thickness.
Intricate Internal Shapes: Ideal for deep ribs, keyways, and splines.
Tool & Die Manufacturing: Used to produce high-precision tools and dies for industrial production.
Advantages of Sinker EDM
Sinker EDM offers several key advantages, making it a valuable tool for complex part production:
Ability to Create Complex 3D Shapes: Perfect for intricate designs where conventional tools fall short.
Low-Stress Machining: As a non-contact process, it avoids mechanical stresses on both the electrode and workpiece.
Precision for Deep Cavities: Ideal for crafting detailed shapes with tight tolerances in hardened metals.
Limitations of Sinker EDM
Despite its strengths, Sinker EDM has certain limitations:
Slower Machining Speed: The process can be time-intensive, especially for high-precision tasks.
High Power Consumption: Requires significant energy, making it less efficient than other machining options.
Limited to Conductive Materials: Sinker EDM only works on conductive metals, limiting its material versatility.

What is Wire EDM?
Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a precise, non-contact method for cutting conductive materials. It uses a charged wire, guided by CNC technology, to create intricate shapes without touching the workpiece.
Wire EDM Process Overview
In Wire EDM, a thin metal wire—usually brass—is fed through a CNC-guided system. This wire, charged with an electrical current, creates sparks between itself and the workpiece. Each spark erodes a small amount of material, shaping the workpiece without physical contact. Deionized water acts as a dielectric fluid, controlling the spark gap, cooling the workpiece, and removing debris. This process enables Wire EDM to cut complex contours and achieve tight tolerances.
Components of a Wire EDM Machine
A Wire EDM machine includes several critical components that ensure precision and control:
Brass Wire: The cutting tool, which is continuously fed to maintain sharpness and accuracy.
CNC Guide System: Guides the wire along programmed paths to create precise cuts.
Deionized Water: Serves as the dielectric fluid, providing controlled conductivity, cooling, and debris flushing.
Applications of Wire EDM
Wire EDM is essential for industries that require high-precision parts. Typical applications include:
Extrusion Dies and Punches: Used for high-precision tools in manufacturing.
Medical Devices: Suitable for small, intricate components in surgical equipment.
Aerospace Components: Ideal for high-precision parts requiring tight tolerances.
Complex Gears and Parts: Produces delicate, detailed parts that conventional tools cannot handle.
Advantages of Wire EDM
Wire EDM offers several advantages that make it highly valuable for precision machining:
High Precision: Can achieve exceptionally tight tolerances, ideal for intricate designs.
Clean Edges: Cuts with no mechanical force, reducing the need for additional finishing.
Versatile for Delicate Cuts: Works well for fine, detailed profiles and parts with tight tolerances.
Limitations of Wire EDM
While Wire EDM is effective, it has limitations:
Material Restrictions: Only works on conductive materials, limiting versatility.
High Initial Cost: Equipment and setup can be expensive, especially for complex applications.
Oxide Layer Formation: May require additional finishing steps to remove surface oxide on certain metals.
Sinker EDM vs Wire EDM: Key Differences
| Aspect | Sinker EDM | Wire EDM |
| Tool Type | Custom-shaped electrode | Thin wire electrode |
| Dielectric Fluid | Hydrocarbon oils | Deionized water |
| Movement | Electrode sinks into the workpiece | Wire moves along X and Y axes |
| Ideal Applications | Molds, dies, blind cavities | Precision profiles, punches, intricate parts |
| Machining Process | Uses a shaped electrode to form complex 3D cavities | Utilizes a continuously moving wire for 2D profile cutting |
| Electrode Type | Custom electrode made of graphite or copper | Thin brass or coated wire |
| Geometry and Capabilities | Best for 3D shapes and blind cavities | Ideal for 2D profiles and fine cuts |
| Surface Finish Quality | Leaves a slightly rougher surface, may require additional finishing | Produces smooth edges with minimal finishing needed |
| Speed and Efficiency | Slower but precise for complex shapes | Faster for thin profiles, continuously cuts material |
| Material Types | Suitable for thicker, more rigid pieces | Better suited for thinner sections and high-precision materials |
| Tolerance and Precision | Precise, especially for deep cavities | High tolerance, ideal for intricate and tight-profile cuts |
| Tooling Requirements | Custom electrodes are required, leading to localized wear | Uses a continuous wire feed, ensuring uniform wear distribution |
| Cost and Operational Impact | Higher cost due to custom electrodes, ideal for low-volume, complex designs | Higher initial setup cost but efficient for high-precision applications |
How to Choose Between Sinker EDM and Wire EDM
Factors to Consider
Production Volume: For small batch or custom parts, Sinker EDM is often ideal, while Wire EDM suits high-precision mass production.
Material Type and Thickness: Sinker EDM handles thicker, rigid materials, whereas Wire EDM excels with thin profiles and delicate parts.
Budget: Initial setup costs for Wire EDM can be higher, but it may reduce costs in high-precision applications.
Surface Finish: Wire EDM generally provides a smoother finish, reducing the need for post-processing.
Part Geometry: Complex 3D shapes or internal cavities are best suited for Sinker EDM, while Wire EDM is ideal for 2D profiles and intricate cuts.
Tolerance Requirements: For extremely tight tolerances, Wire EDM is typically the preferred choice.
When to Use Sinker EDM
Sinker EDM is ideal for projects needing complex 3D shapes, such as:
Mold and Die Making: Excellent for creating injection molds and forming dies.
Blind Cavities: Best for deep cavities and internal features that do not go through the workpiece.
Tooling for Industrial Use: Preferred for creating durable, detailed tools where thickness and structural integrity are crucial.
When to Use Wire EDM
Wire EDM is preferred in applications requiring high precision and clean cuts, such as:
High-Precision Parts: Ideal for aerospace and medical components where accuracy is essential.
Thin Profiles: Suits thin or delicate parts, ensuring no mechanical stress or deformation.
Complex, Tight-Tolerance Cuts: Perfect for intricate profiles and fine cuts that demand strict tolerances.

Conclusion
Sinker EDM and Wire EDM differ significantly in process, applications, and benefits. Understanding each method's strengths and limitations is essential for achieving precise results. Sinker EDM is ideal for creating complex 3D shapes, while Wire EDM excels in high-precision, 2D profile cuts. Consulting EDM experts can help determine the best solution for specific applications, especially in complex manufacturing. Consider factors like part geometry, material type, tolerance requirements, and production volume when selecting between Sinker EDM and Wire EDM to ensure optimal efficiency and precision.
Reference Sources
Electric Discharge Machining
Sinker EDM vs. Wire EDM
FAQs About Sinker EDM and Wire EDM
Q: Is Sinker EDM or Wire EDM More Expensive?
A: Initial setup costs run higher for Sinker EDM due to custom electrode requirements. Wire EDM offers lower setup costs but needs continuous wire replacement. Overall project costs depend on:
Part complexity
Production volume
Material type
Required precision
Q: Can Non-Metal Materials Be Machined Using EDM?
A: No, EDM is limited to electrically conductive materials, making it unsuitable for most plastics and ceramics. For non-metals, consider:
Laser cutting
Waterjet cutting
CNC milling
Q: What is the Accuracy Level of EDM Processes?
A:
| Process | Standard Tolerance | Best Achievable |
| Sinker EDM | ±0.0001 | ±0.00008 |
| Wire EDM | ±0.0001 | ±0.00005 |
Q: What Industries Use Sinker EDM and Wire EDM the Most?
A: Industries requiring precision components use EDM frequently. Aerospace and medical device industries rely on Wire EDM for intricate, high-tolerance parts. Automotive and tooling industries use Sinker EDM for molds, dies, and durable tools with complex internal shapes.
Q: Which EDM Type is Faster?
A: Wire EDM typically operates faster than Sinker EDM, especially for thin profiles or 2D cuts. Sinker EDM is slower but is preferred for deep, complex cavities. Operational speed for both depends on factors like material thickness, part geometry, and required finish.
Looking for EDM manufacturing solutions? Team Mfg delivers both Wire EDM and Sinker EDM services for your production needs.
We support:
Prototype development
Small batch production
Mass manufacturing
Custom projects
Our engineering team brings 10+ years of EDM experience to every project. We focus on quality, speed, and cost efficiency.
Start your project today. Contact Us or call +86-0760-88508730.



















