Threaded holes are crucial in modern manufacturing, serving as the foundation for assembling components securely, providing secure, adaptable, and durable fastening solutions that support both mass production and custom fabrication. This article will reveal everything you need to know about this magical object. Let's take a closer look at the details of threaded holes!
Definition and Types of Threaded Holes
What Are Threaded Holes?
Threaded holes are cylindrical openings designed to accept fasteners like screws or bolts. The internal surface of these holes has a helical ridge—called a thread—that interlocks with external threads on a fastener. This structure creates a strong, friction-based connection, keeping components securely fastened. Threaded holes play an essential role in many industries, including automotive, electronics, and aerospace, where mechanical stability and ease of disassembly are crucial.
Types of Threaded Holes
There are two primary types of threaded holes based on their depth and design: Through Holes and Blind Holes. For a comprehensive overview of different types of holes in engineering, you can refer to our guide on various hole types.
Through Holes: These holes extend entirely through the material, allowing a fastener to pass from one side to the other. They are common in applications where the fastener must penetrate both sides of the workpiece. For instance, in automotive assemblies, through holes enable bolts to be secured with nuts on the opposite side.
Blind Holes: Unlike through holes, blind holes do not extend all the way through the material. The depth is controlled so the fastener doesn’t emerge on the other side. Blind holes often have a flat or cone-shaped bottom and are ideal for applications where aesthetics or functionality demand that the fastener stays hidden, such as in precision electronics or medical devices. For more detailed information on blind holes, check out our article on blind holes in engineering and machining.
To create these threaded holes, machinists use various techniques. Tapping and milling are common methods, but non-machining approaches, like threaded inserts, are also used for softer materials or when additional strength is required. These processes often involve CNC precision machining for optimal accuracy and consistency.
Comparison Table: Through Holes vs. Blind Holes
| Feature | Through Holes | Blind Holes |
| Depth | Extends through the material | Partial depth, does not go through |
| Use Case | When fastener needs to pass through both sides | Aesthetically hidden, fastener does not emerge |
| Bottom Shape | Open on both sides | Typically flat or conical |
Both types offer versatility, but the selection often depends on the project’s structural requirements, aesthetics, or material limitations.
Threaded Holes vs. Tapped Holes
Clarifying the Terminology: Threading vs. Tapping
Confusion often arises when discussing threaded and tapped holes. While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they actually refer to distinct processes and outcomes.
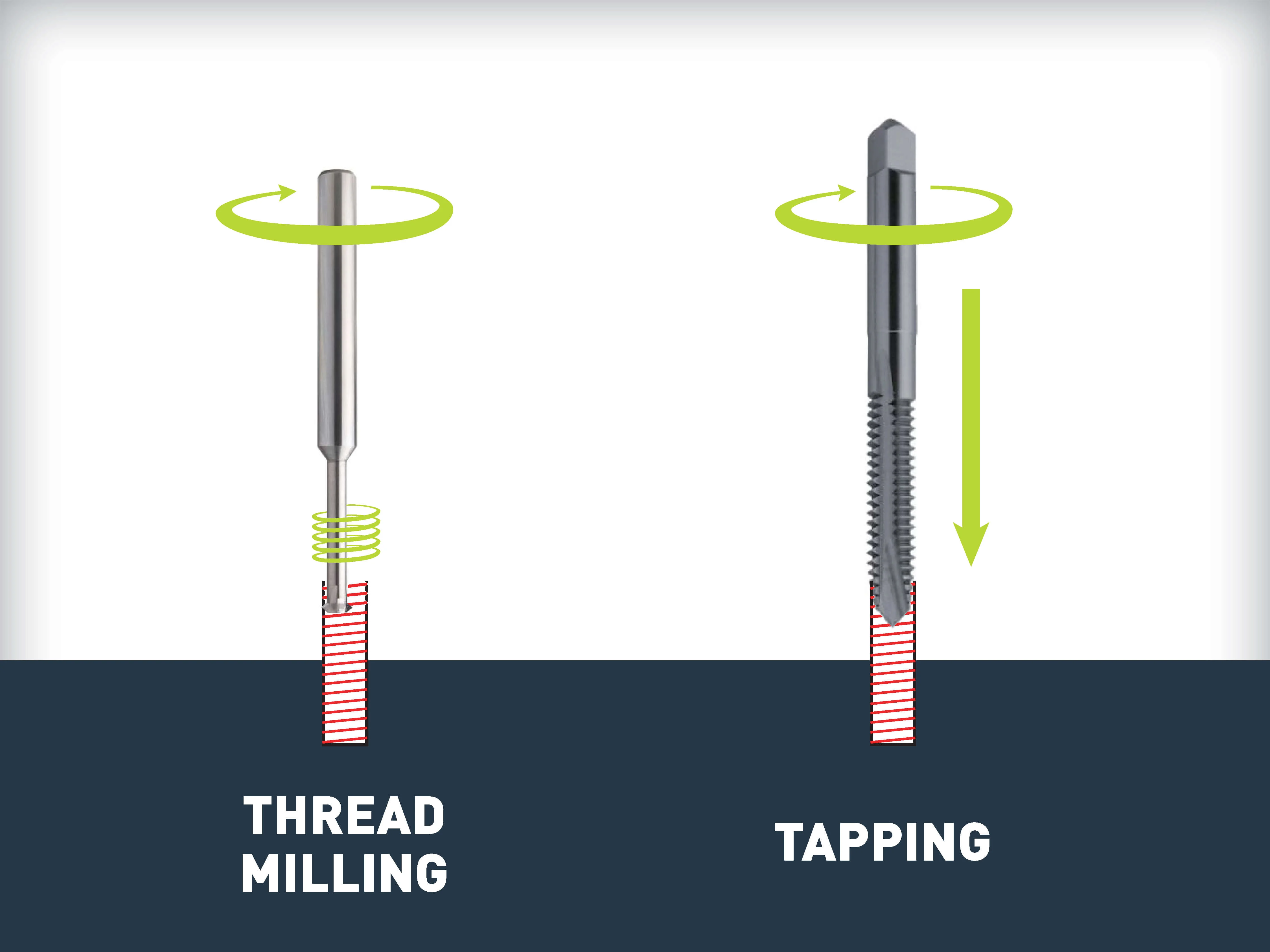
Threading:
Creates external threads on rods, bolts, or screws
Involves cutting helical grooves around the outer surface of a cylindrical object
Tapping:
Produces internal threads inside a pre-drilled hole
Forms threaded cavities in materials like metal, wood, or plastic
Functional and Process Differences
Threaded Holes:
Usually pre-formed during casting or molding
Often found in mass-produced parts
Provide consistent thread quality
May require less post-processing
Tapped Holes:
Created by cutting threads into an existing hole
Offer flexibility for custom applications
Can be performed on-site or as needed
Require precise tooling and skill
| Aspect | Threaded Holes | Tapped Holes |
| Formation | During manufacturing | Post-drilling |
| Consistency | High | Variable |
| Customization | Limited | Highly flexible |
| Tooling | Specialized molds | Taps and drill bits |
| Cost | Lower for high volume | Lower for small batches |
Key Considerations:
Material properties
Required thread strength
Production volume
Assembly requirements
Cost-effectiveness
The Processes Behind Creating Threaded Holes
Forming, Tapping, and Threading: A Comparative Analysis of Methods
Creating threaded holes involves various techniques, each suited to different materials and applications. These processes often utilize CNC precision machining for optimal accuracy and efficiency. Let's explore the main methods:
Forming
Uses pressure to displace material
Creates strong threads without removing material
Ideal for softer metals and plastics
Tapping
Cuts internal threads into pre-drilled holes
Offers precision and versatility
Suitable for a wide range of materials
Threading
Typically refers to creating external threads
Can be applied to internal holes in some contexts
Often used in conjunction with tapping
| Method | Strengths | Limitations |
| Forming | No material waste, strong threads | Limited to softer materials |
| Tapping | Versatile, precise | Can weaken material structure |
| Threading | Efficient for external threads | Less common for internal holes |
Step-by-Step Guide to Making Threaded Holes: Easy-to-Follow Steps
Creating threaded holes doesn't have to be daunting. Follow these steps for success, which can be applied to various types of CNC machines:
Drill the hole: Use a drill bit slightly smaller than the desired thread size. This is called the tap drill size.
Chamfer the hole: Create a small chamfer at the hole entrance using a larger drill bit or a countersink tool. It helps guide the tap.
Lubricate the tap: Apply cutting fluid or oil to the tap. It reduces friction and heat, helping the tap cut more easily.
Start the tap: Place the tip of the tap into the chamfered hole. Apply light pressure and slowly turn the tap clockwise.
Continue tapping: Keep turning the tap. After each half turn forward, reverse the tap a quarter turn to break the chips.
Finish the hole: Continue until the tap has passed through the workpiece or reached the desired depth. Reverse the tap out of the hole.
7.Clean the threads: Use compressed air or a brush to remove any chips or debris from the freshly cut threads.
Pro Tips:
Use a tapping guide for straighter threads
Practice on scrap material first
Take it slow to avoid breaking taps
Types of Taps Used in Hole Threading
Overview of Common Tap Types and Their Uses
Several types of taps are used in hole threading, each with its own characteristics and applications:
Taper Taps:
Have a gradual taper at the cutting end
Ideal for starting threads in blind holes or tough materials
Distribute cutting force over several threads
Plug Taps:
Have a short taper followed by full threads
Used for threading through holes or after a taper tap
Suitable when the hole has an exit point
Bottoming Taps:
Have a very short taper and full threads almost to the end
Used for threading close to the bottom of blind holes
Require a hole deep enough to accommodate the tap
Spiral Point Taps:
Have a spiral flute that pushes chips ahead of the tap
Ideal for through holes in materials prone to long, stringy chips
Commonly used in CNC tapping operations
Spiral Flute Taps:
Have spiral flutes that pull chips back out of the hole
Used for blind holes where chip evacuation is crucial
Help prevent chip packing and tool breakage
| Tap Type | Taper Length | Application |
| Taper | Gradual | Starting threads, blind holes, tough materials |
| Plug | Short | Through holes, after taper tap |
| Bottoming | Very short | Threading close to bottom of blind holes |
| Spiral Point | - | Through holes, materials with stringy chips |
| Spiral Flute | - | Blind holes, chip evacuation |
Choosing the Right Tap for Specific Materials and Applications
Selecting the appropriate tap depends on the material and the hole type:
Soft Materials (Aluminum, Brass, Plastic):
Use a taper or plug tap for through holes
Spiral flute taps work well for blind holes
Higher cutting speeds and coarser pitches are recommended
Hard Materials (Steel, Stainless Steel, Titanium):
Start with a taper tap, followed by a plug tap for through holes
Use a taper tap, then a bottoming tap for blind holes
Slower cutting speeds, finer pitches, and robust lubrication are necessary
Through Holes:
Blind Holes:
Start with a taper tap to guide the threading
Follow with a bottoming tap to thread close to the bottom
Spiral flute taps help with chip evacuation
Helpful Tips for Perfect Threaded Holes
Creating precise, durable threaded holes requires attention to detail and proper techniques. Here are some valuable tips to help you achieve the best results:
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Using the wrong tap drill size:
Failing to chamfer the hole entrance:
Tapping too quickly:
Not using lubrication:
Increases friction and heat, leading to poor thread quality
Apply cutting fluid or oil appropriate for the material
Failing to clear chips:
Can cause chip packing and tool breakage
Reverse the tap to break chips, or use a spiral flute tap for blind holes
Optimizing Accuracy and Durability of Threaded Holes
Use the right tap for the job:
Consider the material, hole type, and thread requirements
Select the appropriate tap type and size
Start the tap straight:
Maintain consistent cutting speed and pressure:
Break chips regularly:
Clean the threads thoroughly:
Removes debris that can interfere with fastener fit
Use compressed air, a brush, or a thread cleaning tool
Verify thread quality:
Check for size, pitch, and form accuracy
Use thread gauges or optical comparators for critical applications
For more information on precision and tolerances, refer to our guide on CNC machining tolerances
| Tip | Benefit |
| Use correct tap drill size | Accurate thread size |
| Chamfer hole entrance | Easier tap starting |
| Control tapping speed | Reduced heat and wear |
| Use lubrication | Improved thread quality |
| Clear chips regularly | Prevent chip packing and breakage |
| Start tap straight | Avoid cross-threading |
| Maintain consistent speed and pressure | Optimal thread quality and tool life |
| Clean threads thoroughly | Ensure proper fastener fit |
| Verify thread quality | Meet accuracy requirements |
For achieving the highest level of precision in your threaded holes, consider utilizing CNC precision machining techniques.
The Importance of Threaded Holes in Manufacturing
Threaded holes play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, providing secure and reliable connections for various components and assemblies.

Key Benefits
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications across industries
Strength: Offer robust and durable connections
Precision: Enable accurate alignment and positioning of parts
Ease of Assembly: Facilitate quick and efficient assembly processes
Reusability: Allow for disassembly and reassembly without compromising integrity
Threaded holes are indispensable in manufacturing, offering a balance of strength, precision, and versatility. Their proper design and implementation are essential for ensuring product quality, reliability, and performance across various industries.
FAQs About Threaded Holes
What are threaded holes used for?
Threaded holes are used to securely fasten components together using screws, bolts, or other threaded fasteners. They are essential in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction for reliable, non-permanent connections.
What is the difference between a threaded hole and a tapped hole?
A threaded hole is any hole with internal threads, created by various methods like tapping, milling, or rolling. A tapped hole specifically refers to a hole where threads are cut using a tap, making it a subset of threaded holes.
How do I choose between blind holes and through holes?
Blind holes are ideal when the fastener shouldn’t pass completely through the material, often for aesthetic or space-saving reasons. Through holes allow the fastener to go all the way through the workpiece, which is preferred for stronger, more secure connections.
What materials can be tapped or threaded?
Most metals (like steel, aluminum, and brass), plastics, and even wood can be tapped or threaded. However, softer materials may require special care or inserts to ensure the threads hold firmly.
What’s the best method for creating threaded holes?
The best method depends on the application. Tapping is cost-effective for standard holes, thread rolling strengthens the surrounding material for high-stress applications, and milling provides precision for custom or complex projects.
How can I prevent thread stripping?
To avoid thread stripping, ensure proper alignment, use the correct fastener size, avoid over-tightening, and apply lubricants when threading. For high-load applications, consider using thread inserts to reinforce the threads.
Can damaged threaded holes be repaired?
Yes, damaged threaded holes can be repaired using techniques like re-tapping or installing threaded inserts like Heli-Coils. These methods restore the threads and maintain the hole's strength.













