Injection molding shapes everyday products, from toys to medical devices. Choosing the right mold is essential for quality and efficiency. In this post, you'll learn the key differences between 2-plate and 3-plate molds, helping you select the best option for your needs.
What is a 2-Plate Mold?
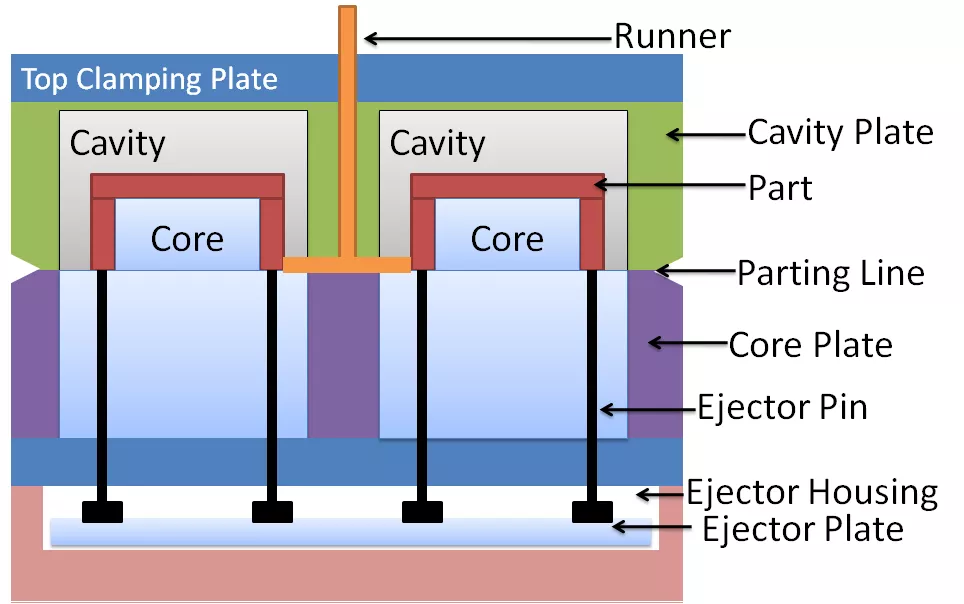
A 2-plate mold, also known as a two-plate mold, is a type of injection molding mold used to manufacture plastic parts. It consists of two main plates: the cavity plate and the core plate.
The cavity plate contains the impression of the final part's outer shape and surface finish. The core plate complements the cavity plate and creates the inner shape of the part.
The injection molding process with a 2-plate mold involves:
Closing the mold, bringing the cavity and core plates together
Injecting plastic material into the cavity under high pressure
Allowing the plastic to fill the cavity and solidify
Opening the mold and ejecting the finished part
Advantages of 2-Plate Molds
Simple design leads to cost-effective manufacturing
Ideal for high-volume production due to shorter cycle times
Well-suited for molding parts with flat or simple geometries
Disadvantages of 2-Plate Molds
Limited flexibility for parts with complex designs or multiple gating points
Single gating point may cause cosmetic defects
Parting line and gate alignment is crucial in multi-cavity molds
What is a 3-Plate Mold?
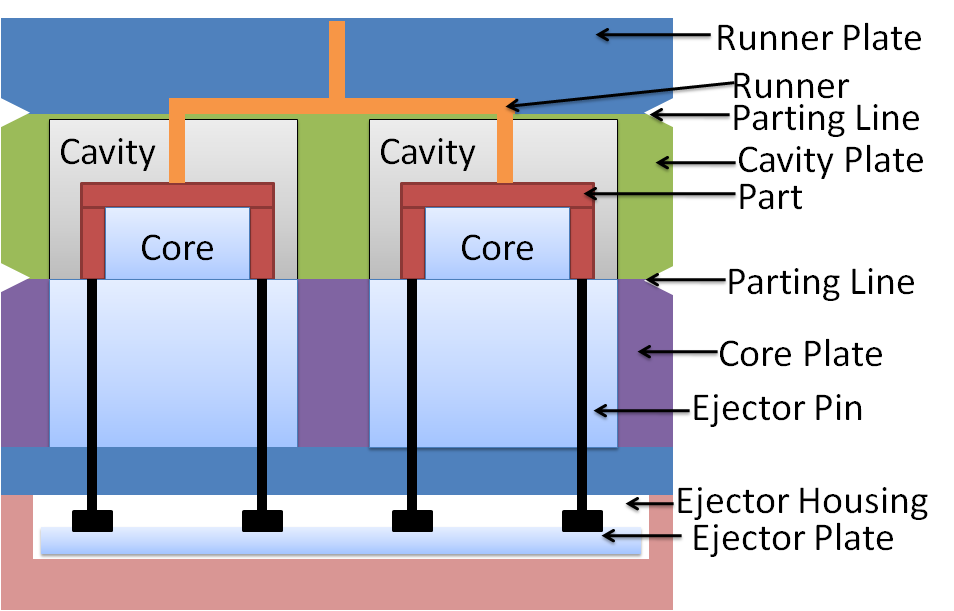
A 3-plate mold, or three-plate mold, is an injection molding tool used to create plastic parts. It has an additional plate called the runner plate or gating plate.
This extra plate sets it apart from the simpler 2-plate mold. The 3-plate mold consists of:
Cavity plate: Contains the impression of the part's outer shape and surface
Core plate: Defines the inner shape of the part
Runner plate: Creates a separate channel for plastic flow into the cavity
The injection molding process with a 3-plate mold involves:
Closing the mold, bringing all plates together
Injecting plastic into the runner system under high pressure
Allowing the plastic to flow through multiple gating points into the cavity
Opening the mold and ejecting the finished part
Advantages of 3-Plate Molds
Versatile for molding complex parts with undercuts or multiple gating points
Reduces cosmetic defects by controlling material flow and strategic gate placement
Offers greater design flexibility and improved part ejection
Disadvantages of 3-Plate Molds
More complex and costly to design and manufacture than 2-plate molds
Longer cycle times due to added complexity
Increased material waste from the runner system
Key Differences Between 2-Plate and 3-Plate Molds
When choosing between 2-plate and 3-plate molds, it's crucial to understand their key differences.
Structural Differences
2-plate molds have a single parting line where the mold splits. In multi-cavity 2-plate molds, the gate and runner are located in this parting plane. 3-plate molds have two parting lines. The additional parting line allows for the runner system to be separated from the molded part.
Functionality Differences
2-plate molds open and close in a single step. When the mold opens, the part and runner remain on the moving side of the mold. The part is then ejected from the same parting surface. 3-plate molds have a more complex opening sequence:
The mold opens, separating the cavity and core plates from the runner plate
The gate breaks away from the part as the runner plate retracts
The part is ejected from the cavity and core plates In 2-plate molds, gate removal is a manual process. 3-plate molds automate this step, as the gate breaks off during the mold opening sequence.
Design Flexibility
3-plate molds offer greater design flexibility. They allow for multiple gating points, making them suitable for complex parts with undercuts or intricate geometries. 2-plate molds are more restrictive in design. They typically have a single gating point, limiting their ability to accommodate complex features or multiple gates.
| Feature | 2-Plate Mold | 3-Plate Mold |
| Parting Lines | Single | Double |
| Runner & Gate Position | In parting plane | Separate from parting plane |
| Mold Opening | Single step | Multi-step sequence |
| Gate Removal | Manual | Automatic |
| Design Flexibility | Limited | Enhanced |
Common Applications
2-plate and 3-plate molds are used across various industries to manufacture a wide range of products. Let's explore some typical applications for each mold type.
Common Applications for 2-Plate Molds
Industry Examples
2-plate molds are commonly used in industries that produce simple plastic parts and consumer goods. These include:
Household items (e.g., kitchenware, storage containers)
Toys and games
Packaging (e.g., bottles, caps, lids)
Product Types
Flat parts and low-precision components are well-suited for 2-plate molding. Examples include:
Simple plastic trays and lids
Promotional items (e.g., keychains, badges)
Basic mechanical components (e.g., gears, pulleys)
Common Applications for 3-Plate Molds
Industry Examples
3-plate molds are often used in industries that require high-precision manufacturing and complex part geometries. Typical industries include:
Automotive (e.g., interior trim, functional components)
Medical (e.g., devices, implants)
Aerospace (e.g., lightweight, intricate parts)
Product Types
Complex shapes and intricate geometries are best suited for 3-plate molding. Specific products include:
Multi-component assemblies
Parts with undercuts or side actions
High-precision gears and mechanical components
| Mold Type | Common Industries | Typical Products |
| 2-Plate | - Consumer goods
- Packaging
- Toys and games | - Simple plastic parts
- Flat components
- Low-precision items |
| 3-Plate | - Automotive
- Medical
- Aerospace | - Complex shapes
- Intricate geometries
- High-precision parts |
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between 2-Plate and 3-Plate Molds
Selecting the right mold type for your injection molding project is crucial. Let's explore the key factors you should consider when deciding between 2-plate and 3-plate molds.
Part Geometry and Design Complexity
The complexity of your part's design plays a significant role in mold selection. 2-plate molds are suitable for simple, flat parts with minimal undercuts. If your part features intricate geometries, undercuts, or requires multiple gating points, a 3-plate mold may be the better choice.
Gating Requirements and Cosmetic Considerations
Consider where you need to place the gate on your part. 2-plate molds typically have a single gating point, which can limit design flexibility and may lead to cosmetic defects. 3-plate molds offer more freedom in gate placement, allowing for strategic positioning to minimize visual imperfections.
Production Volume and Budget
Your production volume and budget also influence mold selection. 2-plate molds are generally more cost-effective for high-volume production of simple parts. They have a lower initial investment and shorter cycle times. 3-plate molds, while more expensive, are valuable for producing complex parts in lower volumes.
Material Properties and Molding Requirements
The material you plan to use and its specific molding requirements should also be taken into account. Some materials may require higher injection pressures or longer cooling times, which can impact mold selection. Discuss your material choice with your injection molding partner to determine the most suitable mold type.
| Factor | 2-Plate Mold | 3-Plate Mold |
| Part Complexity | Simple, flat parts | Complex geometries, undercuts |
| Gating | Single gating point | Multiple gating points |
| Production Volume | High-volume, simple parts | Low-volume, complex parts |
| Budget | Lower initial investment | Higher initial investment |
| Material Properties | Discuss with molding partner | Discuss with molding partner |
Summary
In summary, 2-plate molds are simpler, cost less, and have faster cycle times, while 3-plate molds offer more flexibility and better surface quality. Choosing between them depends on your part's design, production volume, and budget. It's important to balance these factors to ensure efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For complex decisions, consulting with injection molding experts can provide valuable insights and tailored recommendations. This helps ensure you choose the right mold for your specific manufacturing needs.












